Data Structure
A data structure is a specialized format for organizing and storing data.
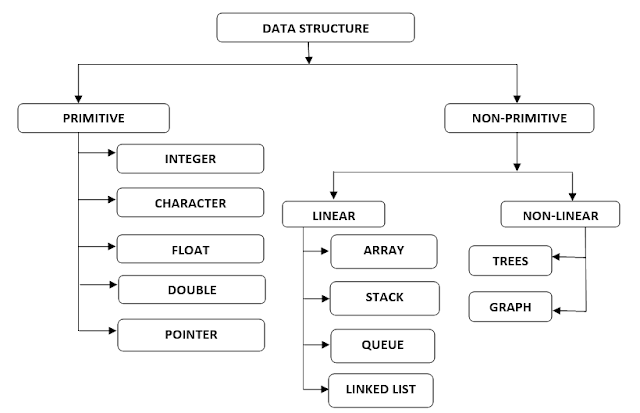
Classification of data structure:
Primitive Data Structure:
Data structures that are
directly operated upon by machine-level instructions are known as primitive
data structure. Examples -
Operations on Primitive Data Structure:
Example: int x;
Select: This operation is
used to access data within a data structure.
Example: cin >> x;
Update: This operation is
used to change or modify the data in a data structure. An assignment operation
is a good example for an update operation.
Example: x = 5;
Destroy: this operation
is used to destroy or remove the data structure from the memory space. Delete
operator is used to perform this operation.
Example: delete x;
When the program
execution ends, the data structure is automatically destroyed, no need to use
delete operator.
Non - Primitive Data Structure:
Data structures that are derived from the primitive data structure are known as non-primitive data structure.
Operations on Non - Primitive Data Structure:
Traversing:
It is the process of visiting each element in the data structure exactly once
to perform certain operations on it.
Sorting:
The process of arranging elements of data structure in ascending or descending
order.
Searching:
The process of finding the location of the element in a data structure is
called searching.
Merging:
It is the process of combining the elements of two data structures into a
single data structure.
Insertion:
The process of adding new data element into the data structure is called insertion.
The data structures in which elements are in a sequence and form a linear series called linear data structure.
Non - Linear Data Structure:
A non-linear data structure is a data structure in which the data element is connected to several other data elements.
Goals of Data Structure:
Efficiency:
the data structure and their operations should be fast and not use more
computer’s resources.
Robustness:
a program produces the correct output for all inputs and handle unexpected
errors.
Reusability: Same code be a component of different systems in various application situations. Software reuse can be a significant cost-saving and timesaving technique.
Comments
Post a Comment